Music and dancing were a major part of Ancient Egyptian culture. Music was especially popular and important during the dynastic periods ruled by pharaohs.

Let’s look at the role music and dance played in the lives of the Ancient Egyptians.
Music in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egyptian music was made by clapping, singing, and playing instruments. It was part of religious ceremonies, funerals, festivals, parties, and small gatherings.
People also used music or chanting at work to ease the boredom of manual labor, like grinding corn.
There were many professional musicians in Ancient Egypt. The status of the musician determined where they could play and sing. Only musicians with a high status could perform for religious ceremonies in the temples.
The highest honor for musicians was to achieve the status of “shemayet,” which meant they were allowed to play for a specific god or goddess. These musicians were mostly women.
Pharaohs and the royal family also had personal musicians of excellent quality. Lower class musicians performed at parties and festivals, where they were often joined by informal singers and dancers too.
Hathor and Bes were the Egyptian gods of music, and many ceremonies devoted to these gods involved music, song, and dance.
Musical Instruments
The Ancient Egyptian had an impressive number of instruments. Their percussion instruments included bells, castanets, hand-held drums, rattles, and a sistrum, which is similar to a tambourine or a triangle.
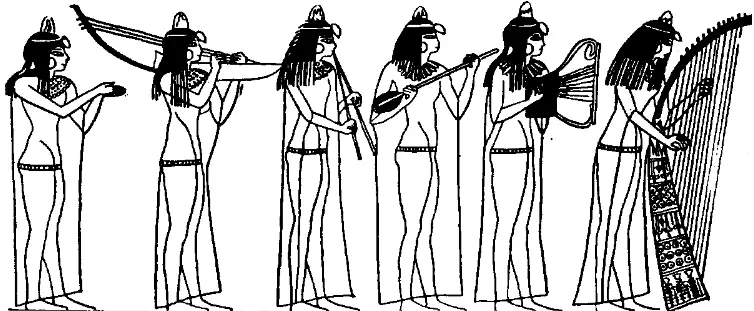
They also had wind instruments like trumpets, flutes, oboes, clarinets, the shepherd’s pipe, and the double pipe.
Stringed instruments were popular as well, including lyres, harps, and the lute.
Historians know that the instruments were valuable to the Ancient Egyptians because instruments have been found with the names of the gods and goddesses carved on them.
The Ancient Egyptians did not use musical notation. They passed songs down by sound from generation to generation.
They did write lyrics, which were often about gods, goddesses, and pharaohs or members of the royal family.
Dance
Ancient Egyptians had many dances: religious dances, non-religious dances, street dances, festival dances, banquet dances, and combat dances.
There were ritual dances that were an important part of religious and funerary rites. One example was the Muu-Dancers, who wore kilts and reed crowns and performed alongside funeral processions.
Dancers performed dramatic and interpretive dances that told stories. Historians believe the genre of the love song may have developed to be accompanied by interpretive dance.
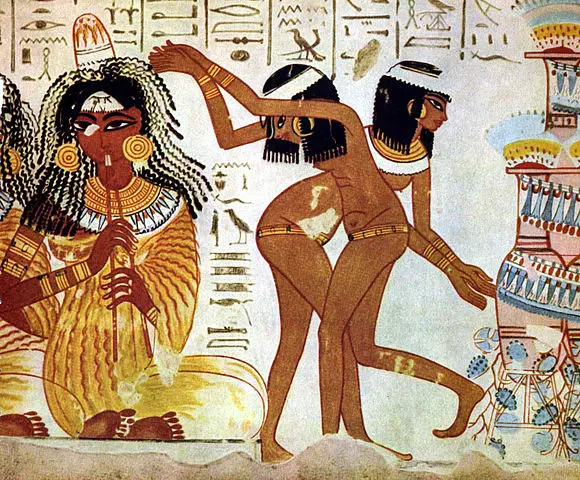

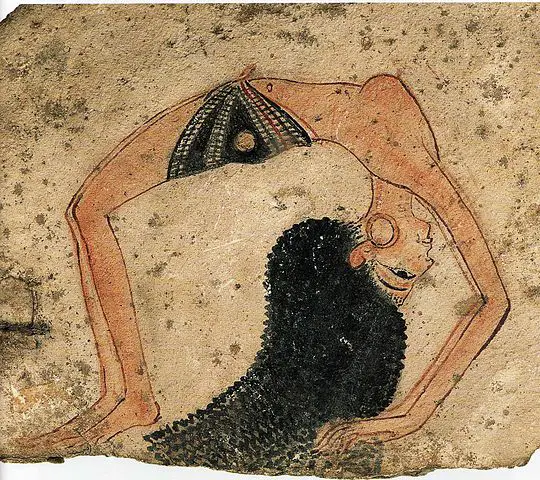
Dancing in Ancient Egypt was very athletic. It included cartwheels, handstands, backbends, and other athletic poses.
Dancers were accompanied by musicians or used hand-clapping or castanets to keep their rhythm.
In all the depictions of dancing, men and women are never seen dancing together. People danced alone, or men danced with men and women danced with women.
Nearly everyone in Ancient Egypt danced, even the pharaohs. However, wealthy people and nobles did not often dance in public like the lower classes.
Other Interesting Facts About Ancient Egyptian Music and Dance
- The movements of Ancient Egyptian dances were named after actions like “the leading along of an animal,” “the taking of the gold,” and, “the successful capture of a boat.”
- The most common drawings and paintings of dancing involve groups of women dancing together, usually in pairs.
- Musicians often wore a menit necklace, a heavily beaded necklace that could be shaken while dancing or taken off and rattled by hand to create music.
- Historians believe that Ancient Egyptians sang in the marketplace and during building projects. For example, the pyramids of Giza were probably constructed to the sounds of music.
- We don’t know what Ancient Egyptian music sounded like, but it may have eventually been influenced by Asiatic and Greek music.
- For the Ancient Egyptians, music held religious meaning, but it was also used as a form of entertainment and celebration.
More Ancient Egypt facts.