About 70% of the Earth’s surface is covered by ocean. It is made up of 321 million cubic miles of water.
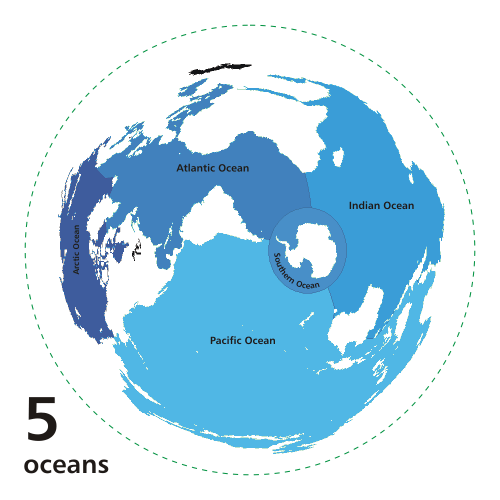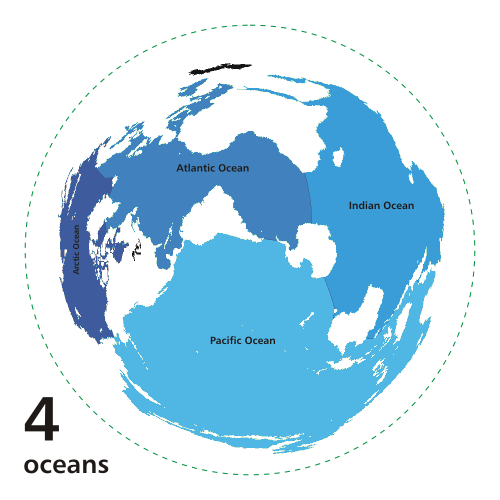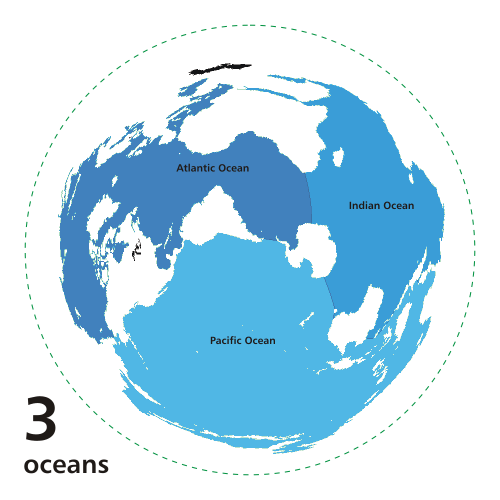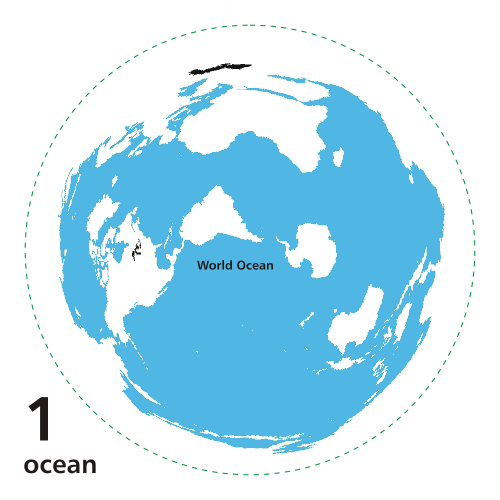
The ocean biome is broken up into five basins: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern.
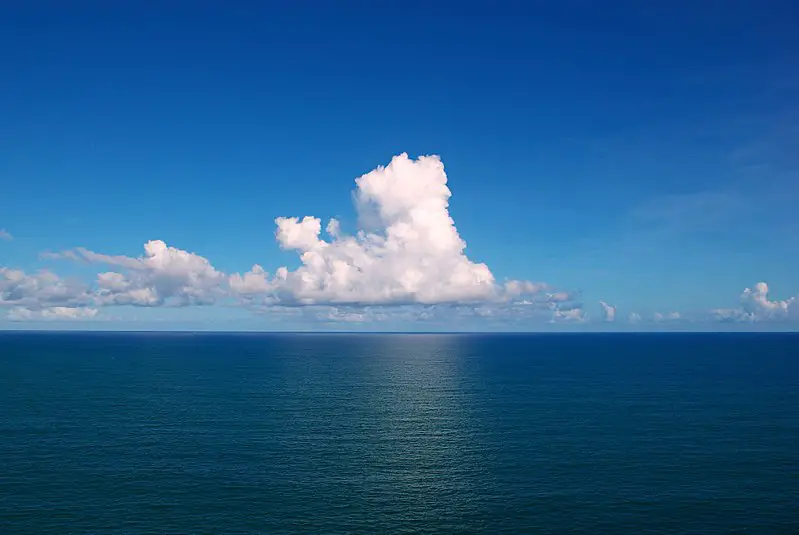

The Different Oceans
The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean. It is 64 million square miles or 28% of the Earth.
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest ocean. It carries warm water in the form of the Gulf Stream to the Northern Hemisphere. Humans travel across the Atlantic more than any other ocean.
The Indian Ocean is larger than Eurasia. Winds and ocean currents switch direction in the Indian Ocean once a year.
The Southern Ocean is the “newest” ocean. Established in 2000, the Southern Ocean is a cold ocean that encircles Antarctica.
The Arctic Ocean is about the size Antarctica on the opposite pole. In winter the Arctic Ocean is covered with pack ice that moves with its currents.
The Oceans and Weather
What happens in the oceans affects the weather of the continents. Water that evaporates from the oceans eventually becomes rain that falls on the land. This is how storms are created.
Oceans are constantly moving. This movement is in the form of currents and waves. Currents move water all over the world, as well as up and down within the ocean. There are two types of currents: surface and deep ocean.
Wind and the Earth’s rotation cause surface currents. Surface currents affect much of the weather patterns on land.
Ocean currents bring warm water to the poles and return cold water to the equator. This helps regulate the Earth’s overall temperature. If it weren’t for currents, temperatures around the world would be extreme, with colder temperatures at the poles and hotter temperatures in the tropics.
Plants
Over 1 million species of plants and animals have been discovered in the ocean, and there may be another 9 million that we haven’t yet discovered!
Some of the most important plants in the ocean are kelp and phytoplankton. Kelp is a form of sea algae that many animals eat. Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that float through the water. Kelp and phytoplankton in the ocean also provide 50% of the world’s oxygen.
Animals
In order to survive in the ocean, many animals have special adaptations. Some have blubber, a thick layer of fat that keeps them warm from the cold ocean water.
Many smaller animals are found in the ocean biome. These animals are crustaceans, fungi, oysters, and bacteria. These animals are a source of food for larger animals in the ocean.
The largest animal in the world, the blue whale, makes its home in the ocean biome. It is over 100 feet long and has a diet mainly of krill and other small organisms.
Other animals that make their home in the ocean are: octopuses, sharks, sea anemone, and turtles.
Interesting Facts:
- There is one cup of salt per gallon of ocean water
- Jellyfish have existed for half a billion years
- More than 80% of the ocean is unmapped
- The average temperature of any ocean is 39 degrees Fahrenheit