What is cell division?
According to cell theory, all cells are made from old cells. They are created through a process called cell division, in which a “parent” cell splits into two identical cells.
In this process, the DNA in the nucleus of the “parent” cell is passed on equally between the two new cells.
Part of the qualifications for something to be classified as a living organism is the ability to reproduce. Cells, being the smallest living things, can reproduce by dividing, which is called asexual reproduction.
It is estimated that as many as two trillion cell divisions could happen within one human body on a daily basis.
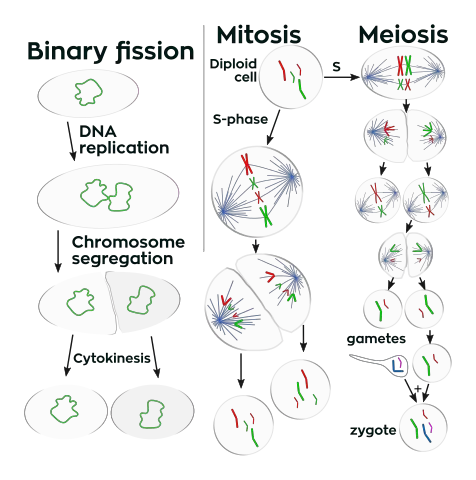
What are the different types of cell division?
Cell division can be classified into three main categories: mitosis, meiosis, and binary fission. Very simple single-celled organisms can reproduce through binary fission, such as bacteria. Binary fission works very similarly to mitosis, but on a smaller scale.
More complicated cells, though, such as the different cells that make up plants and animals, reproduce through mitosis or meiosis.
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a process of cell division that includes replicating one existing cell into two exact copies. In this process, every part of the cell is duplicated to produce identical cells. The previously existing cell is called the parent cell.
The parent cell produces two identical daughter cells, with identical DNA between them. In the human body, blood cells and skin cells both reproduce with mitosis. Mitosis works through a cell cycle, with different phases.
The different phases of the cell cycle include interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
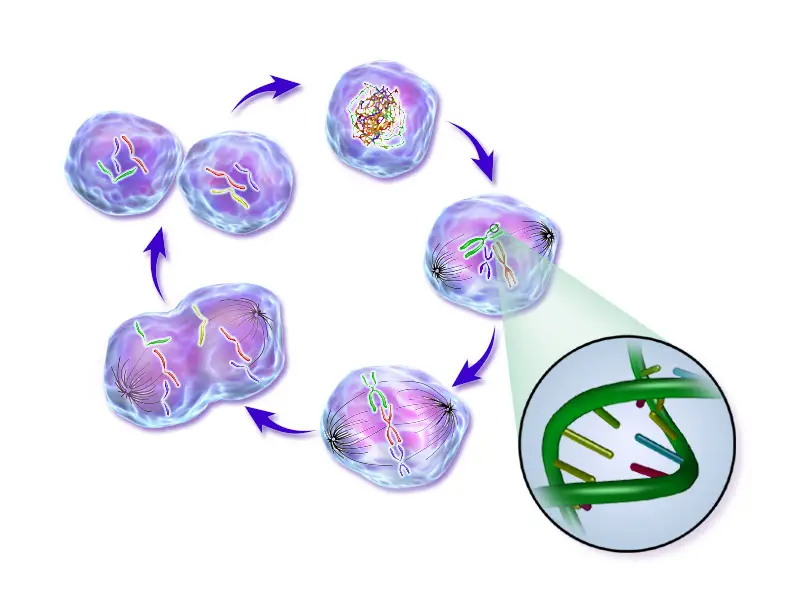
The first phase of genetic material (such as DNA and RNA on the chromatins) cell cycle is interphase, where the cell is in its normal state. During interphase, the DNA in the cell is duplicated.
During the second phase, prophase, chromatins in the nucleus of the cell condense into the form of chromosomes, and the nuclear membrane begins breaking down. During the third phase, metaphase, the new chromosomes line up together in preparation for splitting equally.
During the fourth phase, anaphase, the lined-up chromosomes begin to separate and will travel to opposite sides of the cell from each other. During the last phase, telophase, the cell creates two new nuclear membranes around each of the chromosome sets.
Once the two new nuclear membranes are created, then the wall of the parent cell will pinch together and create a split down the middle of the cell, creating two new daughter cells. The splitting process is called cytokinesis.
What is meiosis?
While binary fission is used to duplicate and reproduce two identical single-celled organisms, and mitosis is used to duplicate and reproduce two identical complex cells, meiosis is the process of reproduction for an entire multicellular organism, such as a human being.
The primary difference between meiosis and mitosis is that mitosis produces two identical cells that share 100% of their DNA, but meiosis produces four new cells that are not identical, and only share 50% of their DNA.
For instance, a human being shares 50% of their DNA with their siblings and each parent. The difference is in identical twins, which share 100% of their DNA.
Questions:
- What are the three types of cell division?
- Which types of cells engage in binary fission?
- What is the first phase of mitosis?
- What happens during cytokinesis?
- How much DNA do daughter cells share from mitosis?

Answers:
- The three types of cell division are binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis.
- Single-celled organisms engage in binary fission.
- The first phase of mitosis is interphase.
- During cytokinesis, a cell splits into two new cells.
- Mitosis results in two daughter cells that share 100% of their DNA.